Prostate cancer is a big health issue for men, hitting millions globally. This guide will give you a deep dive into this condition. You’ll learn about its definition, symptoms, and the newest ways to diagnose and treat it. By the end, you’ll know how to keep your prostate healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland, a small organ below the bladder in men.
- It’s key to catch it early, as treatment works best then.
- Things that raise your risk include age, family history, and lifestyle choices like diet and exercise.
- Symptoms can be trouble urinating, blood in urine or semen, and pelvic pain.
- Tests like the PSA test and digital rectal exams can spot prostate cancer early.
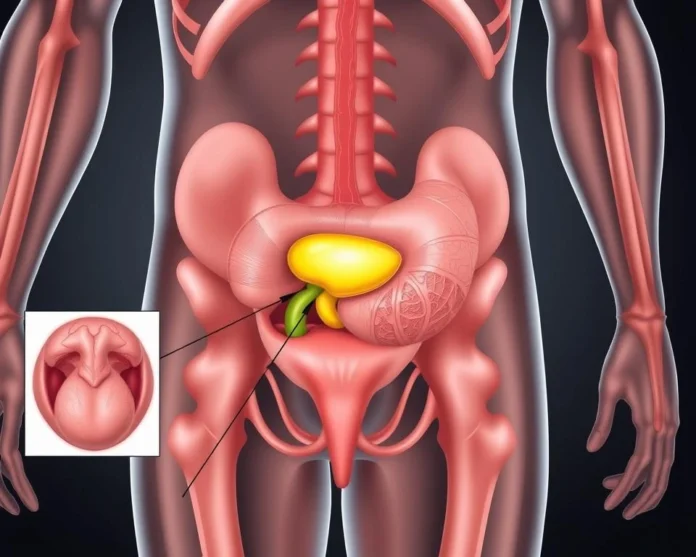
Understanding the Prostate: Function and Anatomy
The prostate is a small, walnut-shaped gland at the base of the male bladder. It’s key to the male reproductive system. Knowing its anatomy and function is vital for health.
Basic Anatomy of the Prostate Gland
The prostate gland has several zones, each with its own role. The central zone makes most of the semen fluid. The peripheral zone is where prostate cancers often start. The transition zone, around the urethra, enlarges with age, causing benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Role in Male Reproductive Health
The prostate gland makes a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. This fluid is crucial for semen. It also helps control urine flow from the bladder.
Common Prostate Problems
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It can lead to urinary issues like a weak stream or frequent need to urinate.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate gland. It causes pain, discomfort, and trouble urinating.
- Prostate cancer: Cancerous cells in the prostate gland. It’s serious if not treated.
Understanding the prostate gland is key to male reproductive health. Regular checkups and screenings can spot and treat issues early.
What Is Prostate Cancer and Its Types
Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland, a small organ below the bladder in men. It happens when cells grow too much and form a tumor. Knowing the types of prostate cancer is key to choosing the right treatment.
Non-metastatic prostate cancer is common. It stays in the prostate and hasn’t spread. This type can be split into two subtypes:
- Non-metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (nmCSPC): This type gets better with hormone therapy, which lowers testosterone.
- Non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC): This type doesn’t get better with hormone therapy and keeps growing.
There are other types too, like metastatic and advanced prostate cancer. Knowing the exact type is vital for a good treatment plan and better results.
| Type of Prostate Cancer | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Non-metastatic prostate cancer | Cancer is confined to the prostate gland and has not spread to other parts of the body. |
| Non-metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (nmCSPC) | Responds to hormone therapy that reduces testosterone levels and slows cancer growth. |
| Non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC) | No longer responds to hormone therapy and continues to grow and spread despite treatment. |
| Metastatic prostate cancer | Cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones or lymph nodes. |
| Advanced prostate cancer | More aggressive and difficult to treat form of the disease. |
Knowing the types of what is prostate cancer helps pick the best treatment. Healthcare providers can make plans that fit each person’s needs. This is true for what is non metastatic prostate cancer and other types.
Risk Factors and Causes of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a complex disease. It can be influenced by many factors. Knowing the causes and risk factors is key for early detection and prevention.
Age and Family History
Age is a major risk factor for prostate cancer. The risk grows as men get older, with most cases in men over 65. A family history of prostate cancer also raises the risk, hinting at a genetic link.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Certain lifestyle choices and environmental exposures may lead to prostate cancer. Eating a lot of red meat and saturated fats increases the risk. On the other hand, a diet full of fruits and vegetables may help protect against it. Exposure to chemicals like asbestos has also been linked to a higher risk of what causes prostate cancer.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a big role in prostate cancer. Inherited genetic mutations, like in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, can make a person more susceptible. Some genetic variants can also affect how aggressive the cancer is.
| Risk Factor | Increase in Risk |
|---|---|
| Age (over 65) | Significantly increased |
| Family History | 2-3 times higher |
| Unhealthy Diet | Moderate increase |
| Asbestos Exposure | Possible association with what causes prostate cancer |
| Genetic Mutations | Significantly increased |
By knowing these risk factors and causes, men can take steps to stay healthy. They can adopt healthier lifestyles and get regular screenings. This helps detect prostate cancer early, when it’s easier to treat.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
It’s vital to know the early signs of prostate cancer for quick diagnosis and treatment. Prostate cancer might not show symptoms at first. But, there are common signs men should watch for. Knowing these 5 warning signs of prostate cancer helps men stay alert and get medical help when needed.
- Difficulty Urinating: Trouble or a change in urination is a common symptom. This includes a weak or interrupted stream, needing to go more often, or feeling like you haven’t emptied your bladder fully.
- Blood in the Urine or Semen: Seeing blood in your urine or semen is a serious sign. It’s important to see a doctor right away.
- Pelvic or Back Pain: Pain in the pelvic area, lower back, or hips that lasts could mean cancer has spread. This is a sign to watch for.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Trouble getting or keeping an erection can be a sign of prostate cancer, especially if it’s advanced.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying can be a symptom of prostate cancer, especially with other symptoms.
Seeing these prostate cancer symptoms doesn’t mean you definitely have it. But, it’s key to get checked by a doctor. This ensures you get the right treatment on time. Regular check-ups and knowing these signs can help manage and treat prostate cancer effectively.
“Early detection is key when it comes to prostate cancer. Paying attention to any changes in your body and speaking with your healthcare provider can make a significant difference in the outcome.”

Diagnosis and Screening Methods
Finding prostate cancer early is key to treating it well. Doctors use several ways to check for prostate cancer. These include PSA tests, digital rectal exams, and biopsies.
PSA Testing
A PSA test checks the blood for prostate-specific antigen. High levels might mean cancer, but can also show other issues. What type of doctor does a prostate exam? Usually, a primary care doctor or urologist will do it.
Digital Rectal Examination
A DRE is a physical check where the doctor feels the prostate through the rectum. It helps see if the prostate is normal. How do you check for prostate cancer? A DRE is often done with a PSA test.
Biopsy Procedures
If tests suggest cancer, a biopsy might be needed. It takes a small prostate tissue sample for cancer checks.
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Performed By |
|---|---|---|
| PSA Test | Blood test that measures prostate-specific antigen levels | Primary care physician or urologist |
| Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) | Physical exam where the doctor feels the prostate through the rectum | Primary care physician or urologist |
| Biopsy | Removal of small samples of prostate tissue for examination | Urologist |
These methods help doctors find and treat prostate cancer. Regular screenings are vital for men’s health.
Stages of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a complex disease with different stages. Each stage has its own treatment options and outlook. Knowing the stages is key to managing the disease effectively.
Prostate cancer is divided into four main stages. These stages are based on the tumor size, spread, and PSA level. Understanding these factors helps in planning treatment.
- Early-Stage Prostate Cancer: This stage is often the most curable. The cancer is small and slow-growing, staying within the prostate. Many men are treated with surgery, radiation, or active surveillance.
- Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer: Here, the cancer has spread but is still in the pelvic area. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy.
- Metastatic Prostate Cancer: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body. While stage 4 prostate cancer is less curable, new treatments help many men manage their condition. Hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies are used.
- Recurrent Prostate Cancer: This occurs when cancer returns after treatment. Additional treatments are needed to manage it.
The stage of prostate cancer can change over time. Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring the disease and adjusting treatment plans.
“With early detection and prompt treatment, many men with prostate cancer can achieve long-term survival and a good quality of life.”
Improving curability and survival rates depends on early screening and diagnosis. Personalized treatment plans are also key.
Treatment Options and Approaches
Prostate cancer is a complex condition, but modern medicine offers many effective treatments. These include surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy. The healthcare team tailors the treatment to each patient’s needs and cancer stage.
Surgery and Radiation Therapy
Surgery or radiation therapy is often the main treatment for many patients. Radical prostatectomy, removing the prostate gland, is common for early cancer. Radiation therapy, like external beam and brachytherapy, can also be effective, preserving the prostate gland.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is a key treatment for prostate cancer. It blocks or lowers male hormones, slowing cancer growth. This is especially helpful for advanced or recurrent cancer, including enlarged prostates.
Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
Chemotherapy or immunotherapy may be used for advanced prostate cancer. Chemotherapy kills cancer cells, while immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system. These treatments can be used alone or with others, based on the patient’s condition and healthcare team’s advice.
The best treatment for enlarged prostate or advanced cancer depends on several factors. These include the cancer’s stage, the patient’s health, and personal preferences. Working with healthcare providers, patients can find the right treatment plan for their prostate cancer.
Living with Prostate Cancer: Lifestyle Changes
Getting a prostate cancer diagnosis can be scary. But, making good lifestyle changes can really help your life and maybe even help you get better. Whether you’re how i cured my prostatitis or dealing with prostate cancer’s long-term effects, these changes can make a big difference.
Embrace a Healthy Diet
Eating well is key in managing prostate cancer. Eat more plant-based foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Fruits, veggies, and whole grains give you important vitamins and minerals. They help fight inflammation and keep you healthy.
Stay Active and Exercise Regularly
Exercise is great for your mood, energy, and even fighting prostate cancer. Do a mix of cardio like walking or swimming and strength training. This keeps your muscles and bones strong.
Prioritize Stress Management
Too much stress is bad for your body and mind. Try meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to handle stress. These activities help with the emotional side of living with prostate cancer.
Seek Support and Connect with Others
Joining support groups, online or in person, can be very helpful. It gives you a community and helps with the emotional and practical parts of prostate cancer. Always talk to doctors or counselors if you’re feeling down.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can help manage how i cured my prostatitis and improve your health during your prostate cancer journey.
| Lifestyle Change | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Healthy Diet | Reduced inflammation, improved overall health |
| Regular Exercise | Improved mood, reduced fatigue, potential to slow cancer progression |
| Stress Management | Enhanced physical and mental well-being |
| Seeking Support | Emotional and practical guidance, sense of community |
“Making lifestyle changes during my prostate cancer treatment was one of the best decisions I’ve ever made. It helped me feel more in control and gave me a sense of empowerment.”

Prevention Strategies and Risk Reduction
Prostate cancer is a serious health concern. But, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. By adopting healthier lifestyle habits and staying vigilant with regular screenings, you can protect your prostate health.
Dietary Recommendations
A well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet is key to how to avoid prostate cancer. Experts suggest eating more plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are full of antioxidants that help fight cancer. Also, try to eat less red and processed meats, and high-fat dairy products.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can lower your risk of prostate cancer. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, most days. Strength training exercises are also good, as they help keep your weight healthy, which is important for how to prevent prostate cancer.
Regular Health Screenings
Early detection is crucial for prostate cancer. Men over 50 should talk to their healthcare provider about PSA testing and regular digital rectal exams. This way, you can catch any issues early and have better treatment outcomes.
Healthy lifestyle choices and regular screenings can greatly reduce your risk of prostate cancer. By taking these steps, you can take charge of your health and possibly avoid this serious disease.
Support Systems and Resources
Dealing with prostate issues can be tough. Having a strong support system and reliable resources is key. Whether you’re facing a prostate cancer diagnosis or just need info, there are many ways to get help.
Connect with a Prostate Health Specialist
Start by talking to a healthcare pro who knows about who do you see for prostate issues. This could be a urologist, prostate cancer specialist, or men’s health doctor. They offer full care, from diagnosis to treatment and ongoing support.

Join a Prostate Cancer Support Group
Meeting others with similar experiences is very helpful. Prostate cancer support groups, both in-person and online, are great. They offer a safe place to share, learn, and find support. These groups provide resources, educational materials, and a community during tough times.
| Resource | Description | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate Cancer Foundation | Nonprofit organization dedicated to prostate cancer research and patient support | www.pcf.org |
| Us TOO International | Prostate cancer education and support network with local chapters | https://ustoo.org/ |
| American Urological Association | Professional organization providing resources for patients and healthcare providers | www.auanet.org |
You don’t have to face prostate issues alone. Reach out to healthcare pros and support networks. This way, you’ll get the resources and guidance you need during this tough time.
Conclusion
Understanding prostate cancer is crucial for our health. Awareness and proactive steps are essential for prostate health. Knowing how this gland works and its common problems helps us take care of ourselves.
Early detection through screenings and talking to doctors is vital. It can greatly improve life for those with prostate cancer. A healthy lifestyle, including the right diet and exercise, helps lower risk.
Prostate cancer is treatable, and medical progress offers hope. Staying informed and proactive helps us face this challenge. With the right support, we can move forward with confidence and hope.
FAQ
What is a prostate?
The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut. It’s located below the bladder in men. It helps produce a fluid that nourishes and transports sperm.
What is prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that grows in the prostate gland. It’s common in older men and one of the most common cancers in men.
What causes prostate cancer?
The exact causes of prostate cancer are still being studied. But, age, family history, and lifestyle factors like diet and chemical exposure are known risks.
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
Early prostate cancer might not show symptoms. But, as it grows, symptoms can include trouble urinating and frequent nighttime urination. Other signs are blood in urine or semen and pelvic pain.
Can prostate cancer be cured?
Yes, prostate cancer can often be cured if caught early. The chance of cure depends on the cancer’s stage, the patient’s age and health, and the treatment used.
What is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
BPH is a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It causes urinary symptoms like trouble urinating and frequent urination. It’s common in older men and is not cancer.
What are the five warning signs of prostate cancer?
The five warning signs are: trouble urinating, frequent urination, especially at night, a weak or interrupted urine stream, blood in urine or semen, and pelvic pain.
How do you check for prostate cancer?
Tests like a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test are used. If these tests suggest cancer, a biopsy may confirm it.
What is non-metastatic prostate cancer?
Non-metastatic prostate cancer hasn’t spread beyond the prostate gland. It’s more treatable and has a better prognosis than metastatic cancer.
How can I survive stage 4 prostate cancer?
Surviving stage 4 prostate cancer is tough, but possible. Treatments include hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation. Early detection and a personalized treatment plan can improve survival chances.
Can asbestos cause prostate cancer?
Some studies suggest asbestos may increase prostate cancer risk. But, the link is not as clear as it is with lung cancer. More research is needed.
Who do I see for prostate issues?
For prostate issues, see a urologist. They specialize in the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Urologists can diagnose and treat prostate conditions like cancer, BPH, and prostatitis.